EV Charger

Electrical Vehicle Charger
As the world is gearing up to unleash an EV revolution, it is still true that the rate of adaption is slow. Electric Vehicles (EVs) despite being a greener, smoother and cheaper mode of transport does not seem to be practical yet. The reason is two words, Cost and Ecosystem. Currently EV’s are priced substantially at par with Gasoline cars making it a less significant choice for buyers, the advancement in battery technology and government schemes are expected to bring down the cost of EV in Future.
Charging station type :
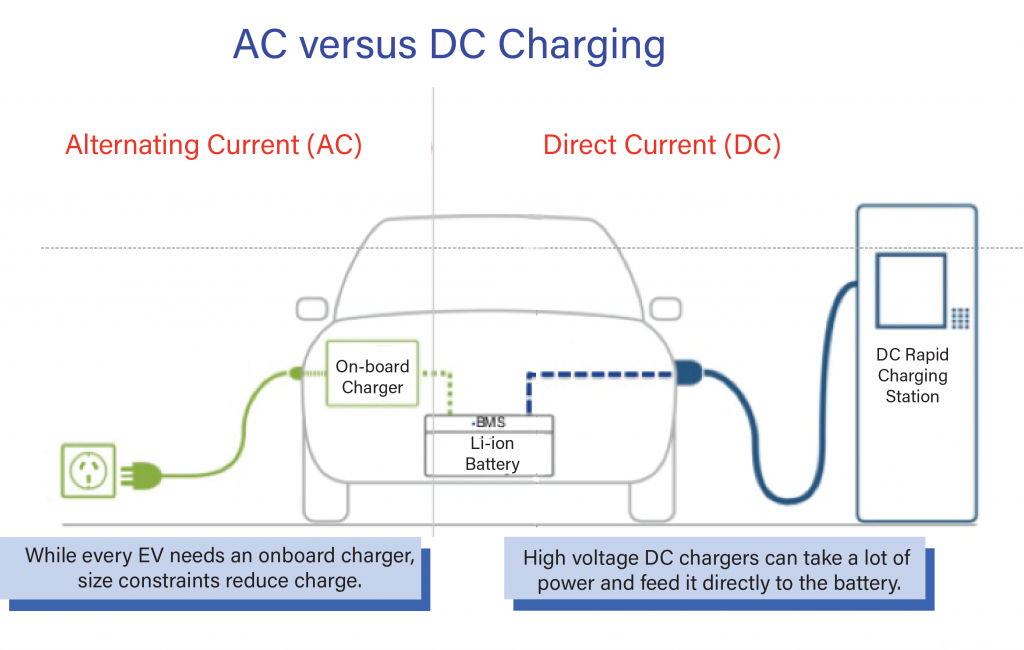
There are mainly two types of charging systems: AC and DC charging systems. The AC charger powers the battery through the vehicle’s on-board charger, while a DC charger directly charges the vehicle’s battery.
level 1:
A Level 1 EVSE is (typically a residential charger) uses commonly available 220 VAC power off the grid, draws current in the order of a 12 A to 16 A range and requires about 8 hours to fully charge a 16 kWH battery.
level 2:
A Level 2 EVSE (typically used in commercial spaces such as malls, offices, etc.) uses three-phase 440 VAC of the grid to power a more robust vehicle charger and draws up to 32A to completely charge a 16 kWH battery in about 8 hours.
level 3:
Level 3 is fast charging station. This type of charging station takes AC power from the grid and then employs a power converter to supply high-voltage (300 V-750 V) DC at up to 400A directly to the vehicle’s battery. Level 3 bypasses the on-board charger on the EV. Since high power is directly supplied into the vehicle, the overall time required to charge is much, lower and explains why Level 3 has earned the name “fast charger.” The charging time for a typical 16 kWH battery is less than 30 minutes.
| Charging Station Type | Charger Level | AC Supply Voltage and Current | Charger Power | Time to charge a 24kWH battery Pack |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC charging Station | Level 1 – Residentia | Single Phase – 120/230V and ~12 to 16A | ~1.44 kW to ~1.92kW | ~ 17 Hours |
| AC charging Station | Level 2 – Commercial | Split Phase – 208/240V and ~15 to 80A | ~3.1 kW to ~19.2 kW | ~120 kW to ~240 kW |
| DC charging Station | Level 3 – Supercharger | Single Phase – 300/600V and ~400A | ~120 kW to ~240 kW | ~ 30 minutes |
Plug Type
Type 1 – single-phase vehicle coupler reflecting SAE J1772/2009 automotive plug specifications
Type 2 – single and three-phase vehicle coupler reflecting the VDE-AR-E 2623-2-2 plug specifications
Type 3 – single- and three-phase vehicle coupler equipped with safety shutters reflecting the EV Plug Alliance proposal
Type 4 – fast charge coupler for special systems such as CHAdeMO
Different between AC and DC
The national grid delivers AC (Alternating Current) but Electric Vehicles must charge their batteries with DC (Direct Current).
An AC charging point/EVSE supplies the vehicle’s onboard charger which in turn converts the AC power to DC allowing the battery to be charged. The size of the onboard charging device is constrained by the space inside the vehicle and price point the manufacturer needs to sell the car. Because the onboard converter is small, the amount of power that they are able to deliver to the battery is typically low (3-6kW).
A DC fast charger bypasses the onboard charging device, supplying power directly and safely to the vehicle’s battery. The DC charger is external to the vehicle and therefore not constrained in size or cost. DC fast chargers use 3-phase power, and have smart technology, enabling them to adjust the charge level to suit the battery state.
Level2 AC wallbox
AC WALL

The wallbox is ideal for residential and commercial locations, businesses in the hospitality industry and those providing overnight charging facilities. It can also supplement DC charging sites for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). It features DC leakage detection, which means there is no need for costly upstream Type-B residual current circuit breakers.
• Easy installation – saves time
• Compact design – saves space
• High quality – more reliability
• DC leakage included – saves extra devices
• Homes
• Offices
• Hotel and Hospitality
• Overnight fleet charging
• Supplement at DC charging sites for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs)
• 4.6kW and 11kW AC charging available
• 22 kW AC fast charging available
• Sealed electronics compartment
• Range of installation options
• Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP). Pro S and Pro M devices can be connected for OCPP 1.5 and load management
• Authentication
• Monitoring
• Load balancing
• Compact design
• Robust all-weather enclosure for indoor and outdoor use Key optional features
• RFID and key authorization
• Input current limiting software to match site requirements
• Web tools for statistics, configuration and access management
• Communication interface for intelligently controlled charging and smart home applications
• Type 1 and type 2 cables available
• Type 2 socket available
• Type 2 with shutter available
• UMTS/G3
• MID certified versions available later in 2018
• Pedestals for 1 or 2 (back to back or 90 degree angle) wallboxes
Level 2 DC wallbox
DC wallbox

The ABB DC wallbox is a compact 24 kW DC fast charger with one or two outlets supporting CCS and CHAdeMO.
Operating the wallbox is easy thanks to a 7” full color, daylight readable touchscreen display. This includes starting and stopping of charge sessions, progress indication during charging, tariff information, help menus, language selection, and PIN code access.
Connectivity is key to success in EV charging. The DC wall box features ABB Ability Connected Services to enable authentication, payment, monitoring, remote diagnostics and repair, as well as over-the-air updates and upgrades.
When charging with AC equipment, charging power is often limited by the onboard converter of the EV. Onboard converters are usually rated 3.3, 6 or 7 kW. Any additional power the AC charging station could provide, remains unused.
With the DC wallbox, 24 kW DC power is provided directly to the battery, bypassing the limitations of the EV’s onboard converter.
• Homes
• Offices
• Car dealerships
• Commercial locations
• 24 kW DC fast charging
• 60 A high output current
• Single or dual outlet: CCS and CHAdeMO
• Daylight readable 7” full color touchscreen display
• Future proof connectivity:
• OCPP
• Capability for remote services
• Compact design
• Robust all-weather enclosure for indoor and outdoor use
• RFID authorization
• On-screen PIN code authorization
• Input current limiting software to match site requirements
• Web tools for statistics, configuration, access management, remote diagnostics and repair
• Integration with back offices and payment platforms
• Customized branding possibilities
The DC wallbox is available in the following configurations:
• Single outlet CCS1
• Single outlet CCS2
• Single outlet CHAdeMO
• Dual outlet CCS1 + CHAdeMO
• Dual outlet CCS2 + CHAdeMO
Level 3 Terra 54 multi-standard DC charging station

Terra 54 CJ is compatible with electric vehicles using the CCS (Combo) standard or the CHAdeMO standard. Typical charging times range between 15 and 30 minutes.
This charger is a cost effective solution to charge all open standard DC capable cars en route. The Terra 54 CJ is also highly suitable to complement an existing AC charging network.
All ABB chargers come with connected services. These allow customers to easily connect their chargers to different software systems like back-offices, payment platforms or energy management solutions via the Inter
• 50 kW DC fast charger supporting CCS, CHAdeMO
And Type 2 AC charging (optional)
• 22 or 43 kW AC cable, or 22 kW AC socket (optional)
• Designed to deliver full output power continuously and reliably over lifetime
• IEC 61000 EMC Class B certified for industrial and
Residential areas (including petrol stations, retail
Outlets, offices, etc.)
• Future proof connection via open industry standards, including remote uptime monitoring and
Assistance, updates and upgrades
• Daylight readable touchscreen display.
• Graphic visualization of charging progress.
• RFID authorization.
• Robust all weather stainless steel enclosure.
• Quick and easy installation.
• Highway petrol / service stations.
• Metropolitan / urban areas.
• Commercial fleet operators.
• EV infrastructure operators and service providers.
Environment : Indoor / outdoor
Operating temperature : -35 oC to +55 oC (de-rating characteristics apply)
Compliance and safety : CE, RCM, EAC, CHAdeMO 1.0
EMC emission : IEC 61000-6-3 Class B – Residential
EMC immunity : IEC 61000-6-2 Industrial
Input AC power connection : 3P + N + PE
Input voltage range : 400 VAC +/- 10%
(50 Hz or 60 Hz)
Max. rated input current & : CJ: 80 A, 55 kV
Power CT, CJT: 112 A, 77 kVA
CJG, CG: 143 A, 98 kVA
Power factor (full load) : > 0.96
Efficiency : 94% at nominal output power
RFID system : ISO/IEC 14443A/B,
ISO/IEC 15393,
FeliCa™ 1, NFC reader mode,
Mifare, Calypso, (option:Legic)
Network connection : GSM / 3G modem,
10/100 Base-T Ethernet
Protection : IP54
Dimensions (D x W x H) : 780 mm x 565 mm x 1900 mm
Mass : 350 kg
